Azure Custom Script Extension On Windows VM and VMSS With Logs
Sometimes it is very useful to be able to run a script on a virtual machine. Luckily, this can be achieved using Custom Script Extension. Its use cases include any configuration or management tasks, for example, software installation and configuration, certificate removal, etc.
NOTE: This works with Windows version of custom script extension. In general, for linux workflow is similar but there are some differences.
In this post we are going to do the following:
- Run custom PowerShell script on Virtual Machine Scale Set (VMSS) and Virtual Machine (VM)
- Specify extension in ARM template in a few ways: as a separate resource, as a part of extensionProfile or as a child resource
- Use Azure Blob Storage for storing custom script and exporting logs
- Retrieve script file from storage account using SAS token or Managed Identity
- Troubleshoot extension installation on VM instance by connecting via RDP
Contents:
- Preparing Custom Script
- About Our Virtual Machine Scale Set
- Adding Extension To ARM Template
- Applying Extension
- Using Managed Identity Instead Of SAS
- Custom Script Extension On Virtual Machine (VM)
- Troubleshooting
Preparing Custom Script
In this section we are going to create our script, put it into a blob storage and make it accessible by leveraging SAS token.
Creating Storage Account and Containers
Here we need to create the following things shown on the screenshot:
- Storage account: for example,
stcontoso - Blob containers:
srcto store our script,logsfor exporting execution logs
Of course, it is up to you how to name them, but in this post we are going to use the names above.
Generating SAS token
Generation of Shared Access Signature token is quite straightforward, just go to “Share access signature” tab and follow the steps.
On the following screenshot we select minimum set of permissions to read and write a blob.
After pressing the button we need to store SAS token value for future use.
Writing Script With Logs
Below you can find a boilerplate code for a PowerShell script which accepts parameter, runs some code wrapped into a try-catch block, writes logs to a file and uploads it to our blob storage.
param (
[string] $SomeParameter
)
# File to write logs
$OutputFile = ".\$($env:COMPUTERNAME).log"
# Removing log file if exists
if (Test-Path $OutputFile)
{
Remove-Item $OutputFile
}
try {
# ...
# Performing operations
# ...
">> !!! My log output, some parameter: $($SomeParameter)" | Out-File $OutputFile -Append
} catch {
">> ERROR:" | Out-File $OutputFile -Append
$_ | Out-File $OutputFile -Append
}
# Uploading log file to blob storage
$Name = (Get-Item $OutputFile).Name
$StorageAccount = "stcontoso"
$Container = "logs"
$SasToken = "?sv=2019-12-12&ss=b&srt=o&sp=rwx&se=2021-01-03T05:36:41Z&st=2021-01-02T21:36:41Z&spr=https&sig=I44%2FLNdN8Gr8EDp%2Fb6lP3jiS7%s0QmzUy21oWNfgO1w%3D"
$Uri = "https://$($StorageAccount).blob.core.windows.net/$($Container)/$($Name)$($SasToken)"
# Setting TLS protocol version to 1.2
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
$Headers = @{'x-ms-blob-type' = 'BlockBlob'}
Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $Uri -Method Put -Headers $Headers -InFile $OutputFile
NOTES:
- Debug script locally to check for syntax errors, log file upload, etc.
- Computer name is used for log filename since we will have many log files from different VMSS instances
- Extension logs can be viewed in
- We can specify any path inside of container where you want to put the log file, for example
https://$($StorageAccount).blob.core.windows.net/$($Container)/prod/westus/$($Name)$($SasToken) - TLS version is set to 1.2 because by default storage account doesn’t accept lower versions, please see screenshot below
Uploading Script To Blob Storage
Just upload your script to src container, as a result, we will have URL like this:
https://stcontoso.blob.core.windows.net/src/MyCustomScript.ps1
About Our Virtual Machine Scale Set
Just a few notes about our sample VMSS to be on the same page:
- Scale set name is
vmss-contoso, image is 2019-Datacenter - Very simple VMSS with 3 instances, probably the cheapest SKU, created through Azure Portal
- Upgrade policy is
Automatic- with this setting instances will upgrade to the latest model immediately - Has a load balancer set up - we’ll use its public IP to RDP to the instances for troubleshooting
- Network security group allows outbound internet traffic - for uploading logs to storage account
Adding Extension To ARM Template
Here comes the most interesting and important part, we are going to add our extension in ARM template. This documentation page contains a lot of useful information including extension schema.
We can add extension via ARM template in three ways:
- Keep extension as a separate resource outside of VMSS definition
- Add extension to
extensionProfileof VMSS - Add extension in a child resources section of VMSS
In the next sections we are going to cover only first two since the last option is just a slight variation of the first one.
Notes about ARM template fields (more information under documentation link above):
name- should consist of two sections because extension is a nested resource: VMSS name and extension namefileUris- our script link with SAS token, however, SAS token is not needed if we use managed identitytimestamp- if custom script extension is already installed, then changing timestamp value triggers rerun of the scriptcommandToExecute- in our case we invoke powershell command and pass custom parameter
Separate Resource Outside Of VMSS Definition
IMPORTANT: If you add extension to the same template where your VMSS is, then remember to specify dependency on VMSS using dependsOn.
{
"$schema": "http://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2015-01-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"parameters": {
"vmssName": {
"defaultValue": "vmss-contoso",
"type": "string"
}
},
"variables": {},
"resources": [
{
"type": "Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachineScaleSets/extensions",
"apiVersion": "2018-06-01",
"name": "[concat(parameters('vmssName'),'/CustomScriptExtension')]",
"location": "[resourceGroup().location]",
"properties": {
"publisher": "Microsoft.Compute",
"type": "CustomScriptExtension",
"typeHandlerVersion": "1.10",
"autoUpgradeMinorVersion": true,
"settings": {
"fileUris": [
"https://stcontoso.blob.core.windows.net/src/MyCustomScript.ps1?sv=2019-12-12&ss=b&..."
],
"timestamp": 202101021
},
"protectedSettings": {
"commandToExecute": "powershell -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -File MyCustomScript.ps1 -SomeParameter \"foobar\""
}
}
}
]
}
VMSS extensionProfile
{
"$schema": "http://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2015-01-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"parameters": {
"vmssName": {
"defaultValue": "vmss-contoso",
"type": "string"
}
},
"variables": {},
"resources": [
{
"type": "Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachineScaleSets",
"name": "[parameters('vmssName')]",
"...": "",
"properties": {
"...": "",
"virtualMachineProfile": {
"...": "",
"extensionProfile": {
"extensions": [
{
"name": "CustomScriptExtension",
"properties": {
"publisher": "Microsoft.Compute",
"type": "CustomScriptExtension",
"typeHandlerVersion": "1.10",
"autoUpgradeMinorVersion": true,
"settings": {
"fileUris": [
"https://stcontoso.blob.core.windows.net/src/MyCustomScript.ps1?sv=2019-12-12&ss=b&..."
],
"timestamp": 202101021
},
"protectedSettings": {
"commandToExecute": "powershell -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -File MyCustomScript.ps1 -SomeParameter \"foobar\""
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
]
}
Applying Extension
There are multiple ways to add extension to VMSS, some of them:
- Deploy a custom ARM template in Azure Portal
- Apply ARM template as part of CI/CD
- Add extension using Azure PowerShell
- Use VMSS extensions tab in Azure Portal to add extension through UI
In this post we will briefly discuss only two of them: deploying custom template in portal and adding extension through VMSS UI.
Custom Template Deployment In Azure Portal
Follow these steps to submit your ARM template:
- Search for “deploy” in the top bar, select “Deploy a custom template”
- Press “Build your own template in the editor” and upload your template
- Select correct resource group and create deployment
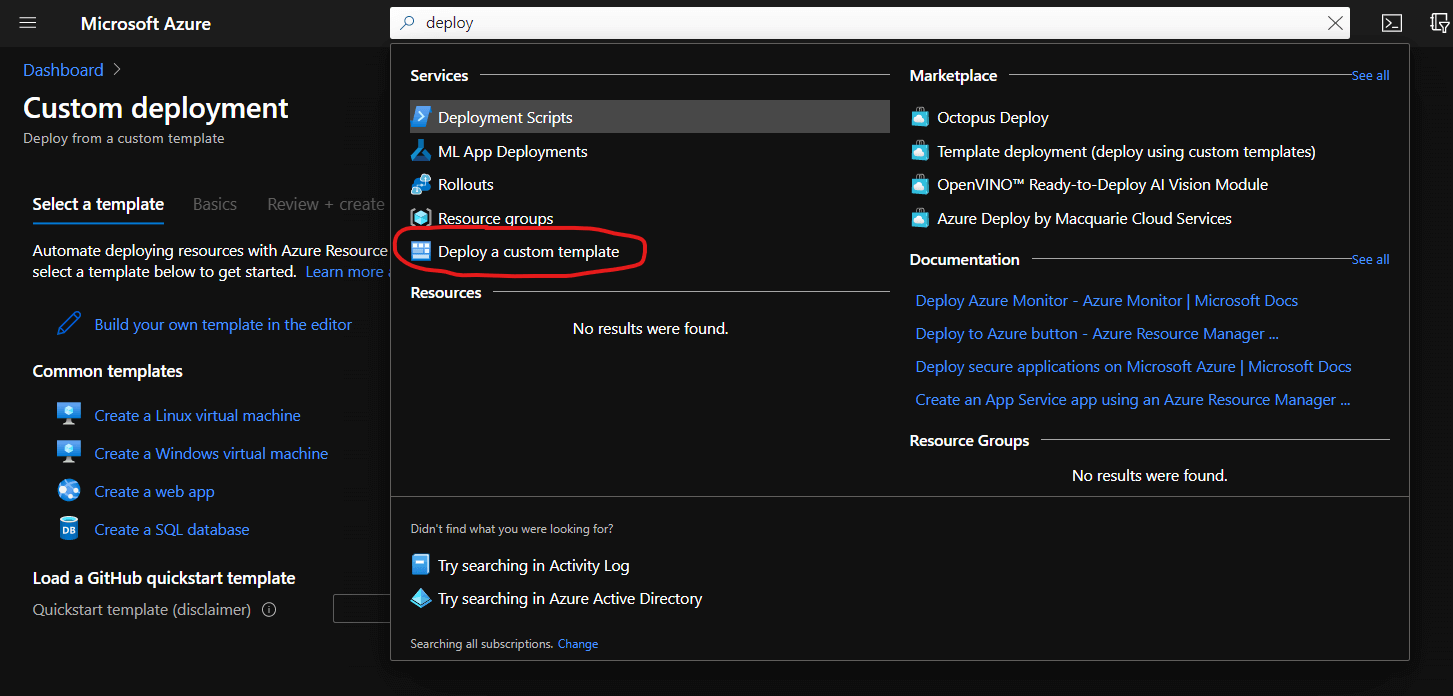 Custom Deployment - Azure Portal
Custom Deployment - Azure Portal
Viewing Logs
When deployment completes you should see logs in the storage account. Each file corresponds to a virtual machine instance, in our sample case we have 3 instances and, thus, 3 log files.
Here is an example output from the script we created:
VMSS Extensions Tab
This is a possible way to add extension to our VMSS, however, it is much less flexible than using ARM template. For example, at the time of writing it seems like we can only use storage account to keep a custom script and this storage account has to be in the same region. Also, not sure how to edit existing extension and control parameters like timestamp.
As you might think, I strongly prefer ARM templates in this case. But feel free to try VMSS UI as well, it could be sufficient for your needs.
To add extension through UI:
- Go to VMSS page in Azure Portal
- Select “Extensions” tab and press “Add” button
- Choose “Custom Script Extension” from the list
- Specify script location and arguments your script requires
Using Managed Identity Instead Of SAS
In this section we cover how to use system assigned managed identity to download our script. Applying user assigned managed identity is almost identical, this link might help.
IMPORTANT: This only covers retrieving the custom script from blob storage using managed identity but assumes that we still use SAS token for uploading logs.
1. Enable System Assigned Identity
Go to VMSS (or VM) page, select “Identity” tab and flip status to “On” for System assigned option.
Of course, you can configure it through ARM template as well.
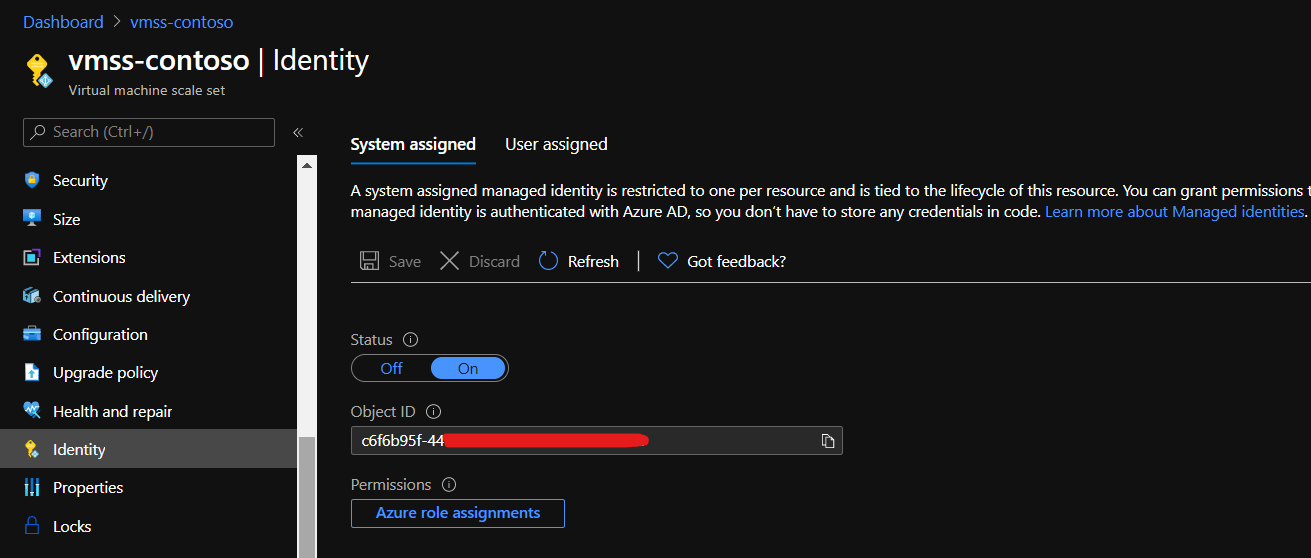 System assigned Managed Identity
System assigned Managed Identity
2. Give Permissions To Managed Identity
Assign “Storage Blob Data Reader” role to the managed identity created in the previous step. It might take some time for this assignment to take effect.
The result should look like the following:
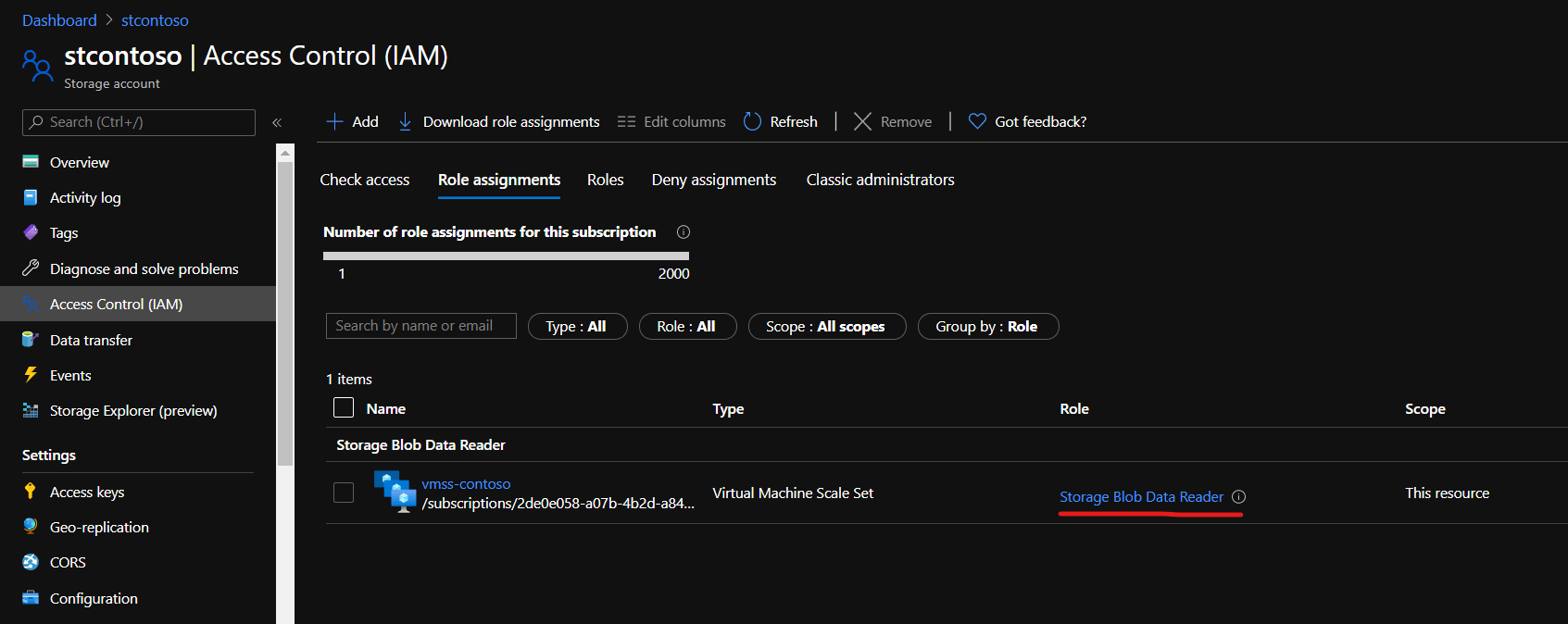 Assigned Role to Managed Identity
Assigned Role to Managed Identity
3. Add managedIdentity Field to ARM Template
Here we just need to add "managedIdentity": {} as part of protectedSettings. The value is empty JSON object because we use system assigned managed identity. About user assigned identity read here.
NOTE: Our script URI doesn’t need SAS token anymore, see example below.
{
"$schema": "http://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2015-01-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"parameters": {
"vmssName": {
"defaultValue": "vmss-contoso",
"type": "string"
}
},
"variables": {},
"resources": [
{
"type": "Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachineScaleSets/extensions",
"apiVersion": "2018-06-01",
"name": "[concat(parameters('vmssName'),'/CustomScriptExtension')]",
"location": "[resourceGroup().location]",
"properties": {
"publisher": "Microsoft.Compute",
"type": "CustomScriptExtension",
"typeHandlerVersion": "1.10",
"autoUpgradeMinorVersion": true,
"settings": {
"fileUris": [
"https://stcontoso.blob.core.windows.net/src/MyCustomScript.ps1"
],
"timestamp": 202101021
},
"protectedSettings": {
"commandToExecute": "powershell -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -File MyCustomScript.ps1 -SomeParameter \"foobar\"",
"managedIdentity": {}
}
}
}
]
}
Custom Script Extension On Virtual Machine (VM)
We have already covered a lot of things regarding custom script extension and used VMSS as an example, this is because documentation covers virtual machine case quite well.
For the VM case compared to VMSS the only difference is in ARM template part, there’s no extensionProfile case for VMs. Script creation and preparation, SAS token or system assigned managed identity will be similar for virtual machine.
Almost all sections are still relevant for VM case:
Below is ARM template for our extension, key points:
- Assuming that virtual machine name is
vm-contoso - Extension type is
Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/extensions - Remember to add dependency on VM resource inside of
dependsOnsection if you deploy VM and extension in the same ARM template
{
"$schema": "http://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2015-01-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"parameters": {
"vmName": {
"defaultValue": "vm-contoso",
"type": "string"
}
},
"variables": {},
"resources": [
{
"type": "Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/extensions",
"apiVersion": "2018-06-01",
"name": "[concat(parameters('vmName'),'/CustomScriptExtension')]",
"location": "[resourceGroup().location]",
"properties": {
"publisher": "Microsoft.Compute",
"type": "CustomScriptExtension",
"typeHandlerVersion": "1.10",
"autoUpgradeMinorVersion": true,
"settings": {
"fileUris": [
"https://stcontoso.blob.core.windows.net/src/MyCustomScript.ps1?sv=2019-12-12&ss=b&..."
],
"timestamp": 202101021
},
"protectedSettings": {
"commandToExecute": "powershell -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -File MyCustomScript.ps1 -SomeParameter \"foobar\""
}
}
}
]
}
Troubleshooting
Sometimes our custom script extension is not working and this is fine. Let’s see some things you might want to check first:
- Script is downloadable from VMSS, for that either URI should contain SAS token or managed identity access should be configured
- For logs export, verify that inside of the custom script an upload URI contains valid SAS token
- To apply new version of the already installed extension, change
timestampvalue - Network security group should allow outbound internet traffic - otherwise VMs won’t have connectivity to blob storage
- Upgrade policy is set to Automatic - if it is Manual your latest VMSS model won’t be applied automatically but you still can trigger update manually
View Extension Installation On VM using RDP
If nothing above helps, we can connect to our VMSS instances and view actual extension configuration and logs.
In this post we are not going to discuss how to connect to instances via RDP. But if you have issues connecting and your load balancer is of SKU “Standard”, then you might want to try to add inbound rule for network security group used for your VMSS.
Extension should be installed under following path (the last segment is version, so it could be different in your case):
C:\Packages\Plugins\Microsoft.Compute.CustomScriptExtension\1.10.9
 Extension installation folder on VM
Extension installation folder on VM
NOTES:
Downloads- contains downloaded versions of our scriptRuntimeSettings- extension settings including what we specified in ARM templateStatus- contains extension execution results, you will find error messages if something failed. Successful status file looks like the JSON below
[
{
"version": "1",
"timestampUTC": "2021-01-02T23:56:55.6741325Z",
"status": {
"name": "SecureCommand_2",
"operation": "Command Execution Finished",
"status": "success",
"code": 0,
"formattedMessage": {
"lang": "en-US",
"message": "Command execution finished"
},
"substatus": [
{
"name": "StdOut",
"status": "success",
"code": 0,
"formattedMessage": {
"lang": "en-US",
"message": "\r\n"
}
},
{
"name": "StdErr",
"status": "success",
"code": 0,
"formattedMessage": {
"lang": "en-US",
"message": ""
}
}
]
}
}
]
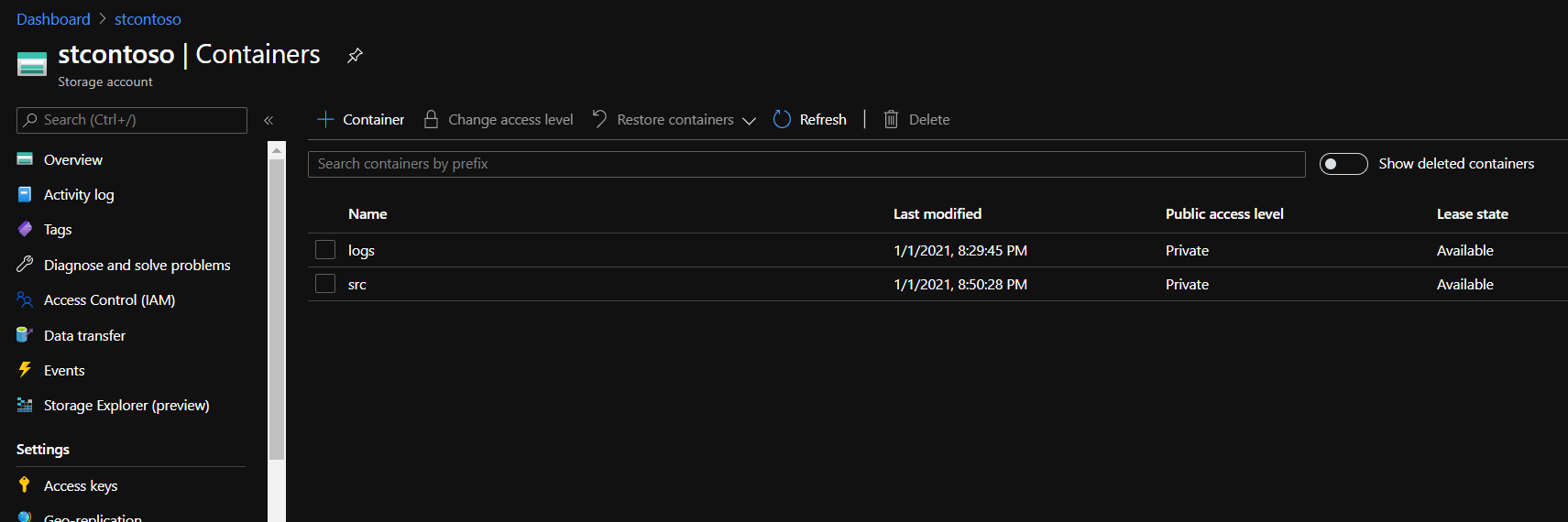 Storage Account Containers
Storage Account Containers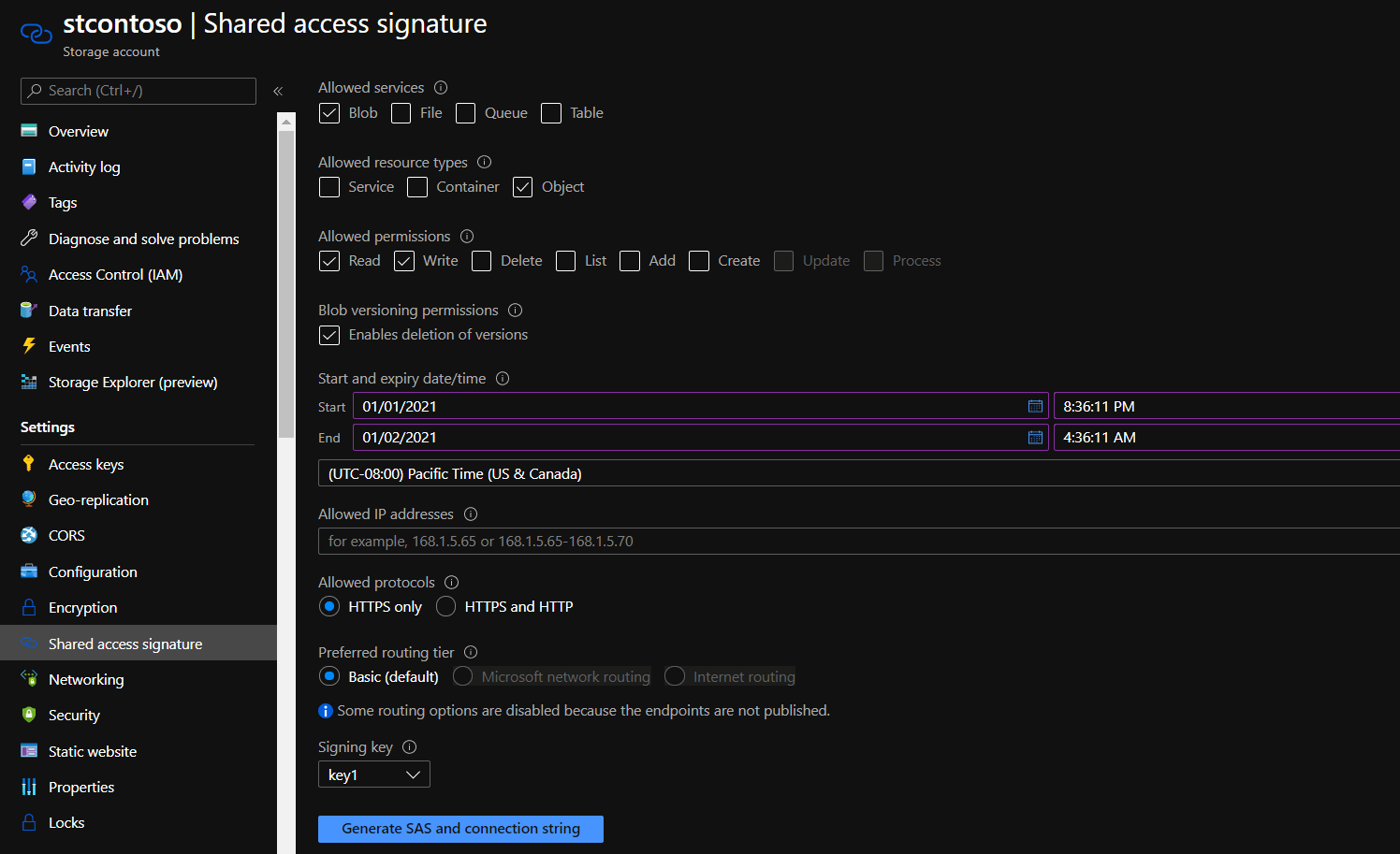 Shared Access Signature
Shared Access Signature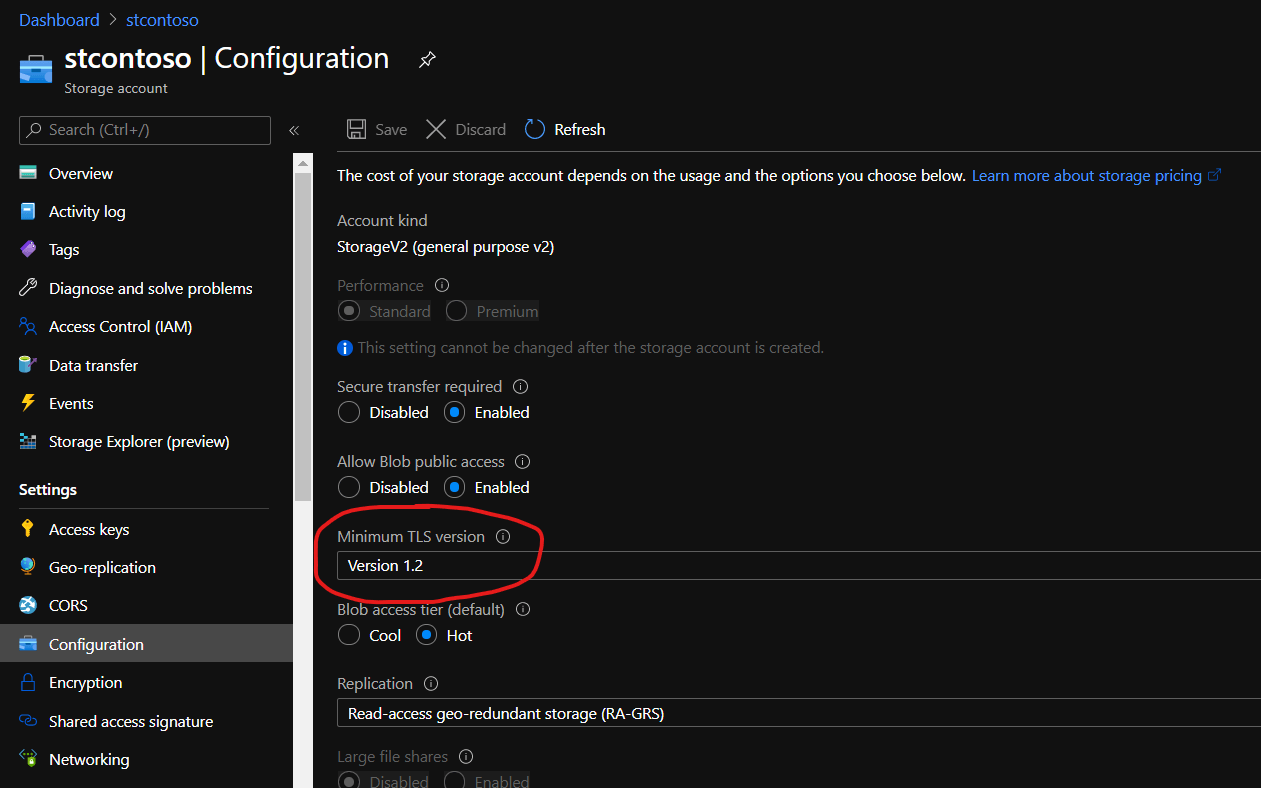 Minimum TLS version
Minimum TLS version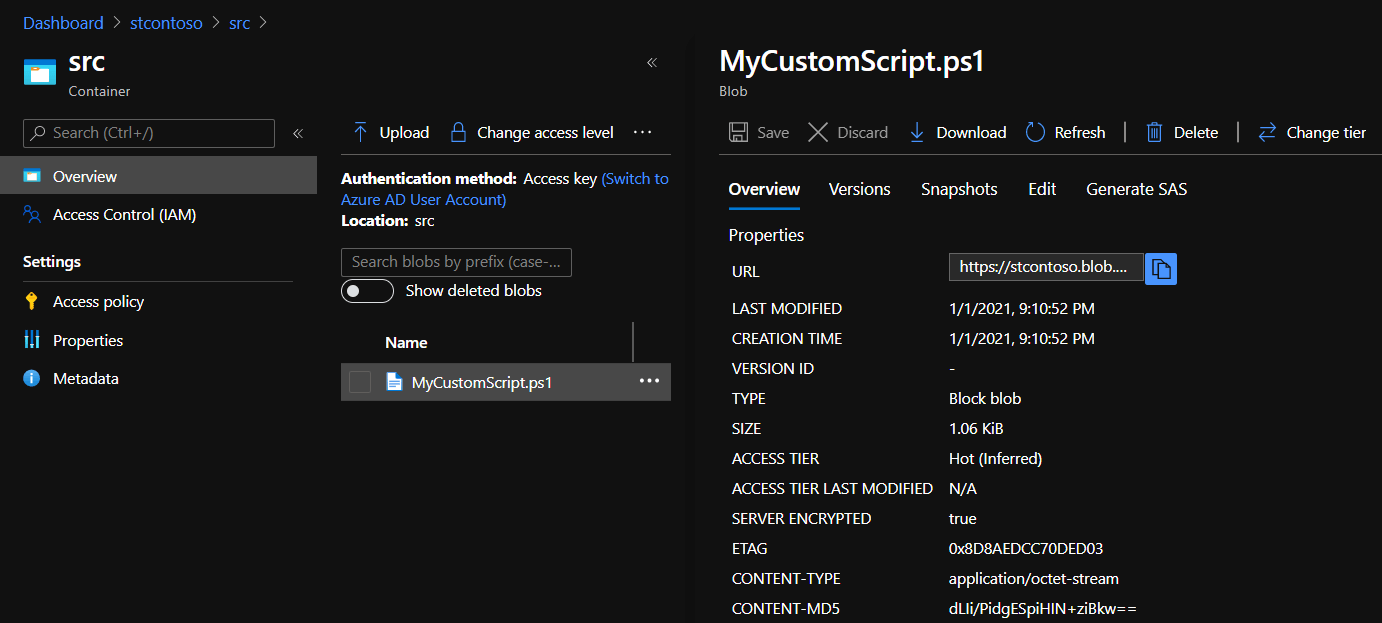 Uploaded custom script
Uploaded custom script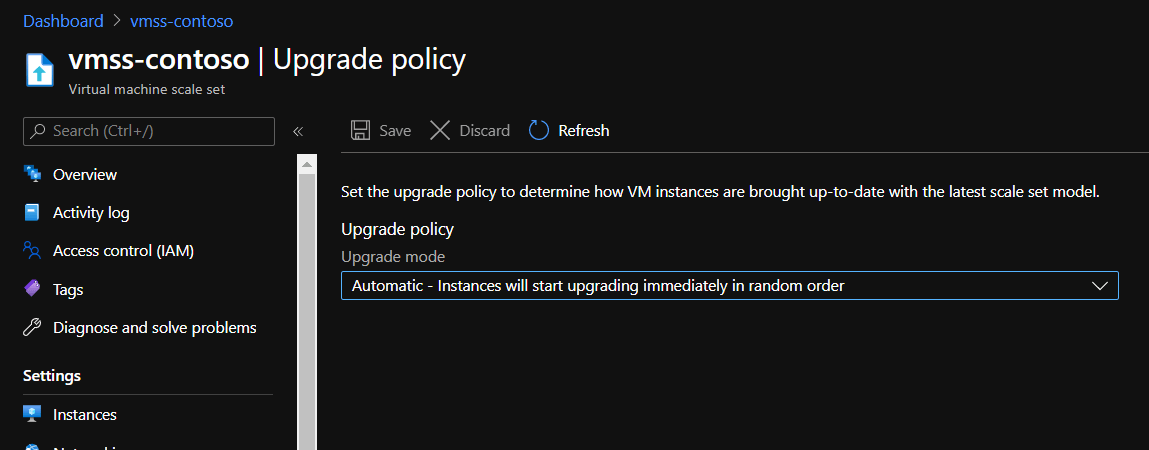 Upgrade Policy Automatic
Upgrade Policy Automatic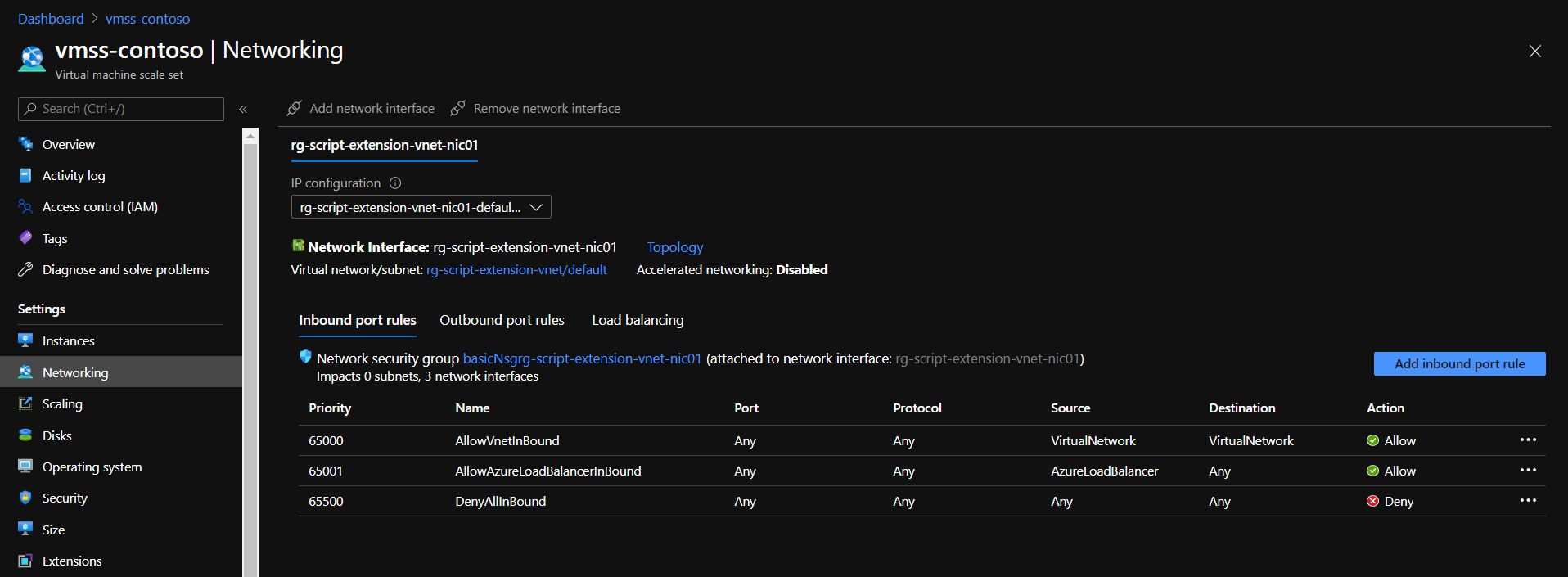 VMSS Networking
VMSS Networking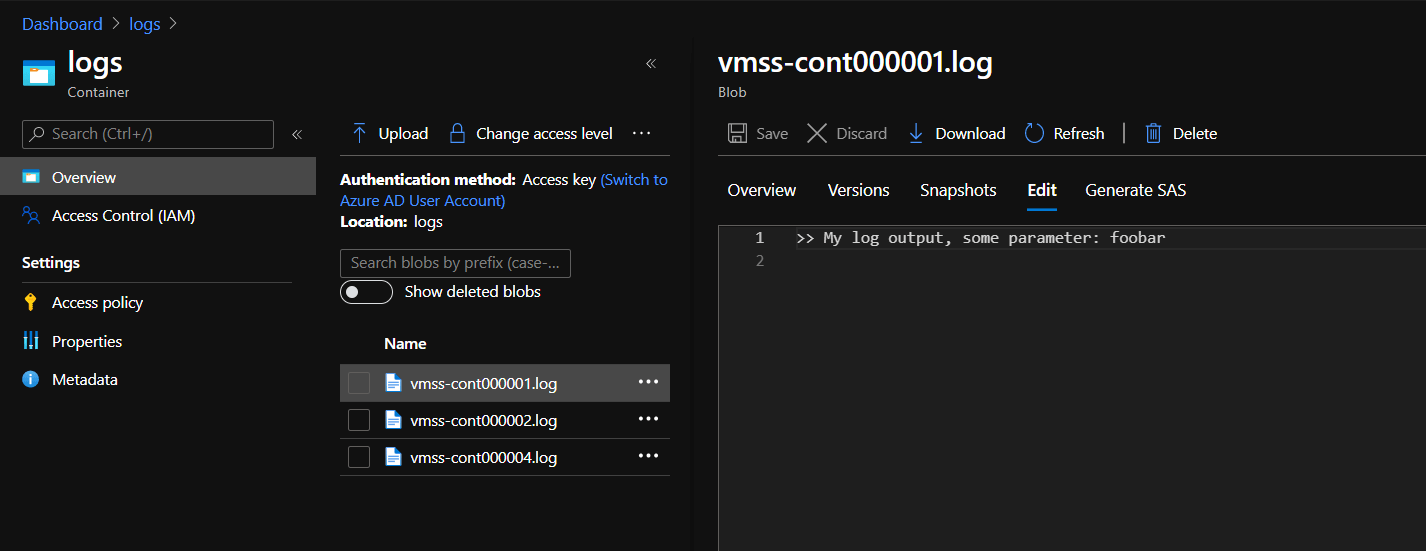 Logs in Storage Account
Logs in Storage Account