Install PowerShell Module From Azure Artifacts Feed In CI/CD Pipeline
In this post we will learn how to install PowerShell module in build/release pipeline from private feed in Azure DevOps without using Personal Access Tokens (PAT).
To get access to the feed and install module it is possible to use System.AccessToken that is provided by the execution environment and has access to Azure Artifacts feeds.
We will cover how to do this in both Classic and YAML Pipelines in Azure DevOps. Classic Pipeline’s case will be used to give more detailed explanation and then easily translated to YAML pipeline’s case.
Why is it better to use System.AccessToken?
Personal Access Token (PAT) is not a good way to get resource access in CI/CD pipeline since PAT is tied to a particular user and also has an expiration date. However, it is okay to use it in your local environment.
System.AccessToken is a better choice in the case of CI/CD pipeline since it is dynamically generated by Azure Pipelines for each job at run time. Hence, there is no need to worry about expiration and token ownership.
Classic Pipeline
This section walks through the steps to achieve our goal using Classic Web UI of Azure Pipelines.
1. Enable Access To OAuth Token For Scripts
By default System.AccessToken is not available in scripts, we need to enable it in Agent Job settings as shown on the screenshot below.
After enabling it, we will be able to access this token through $env:SYSTEM_ACCESSTOKEN variable in PowerShell.
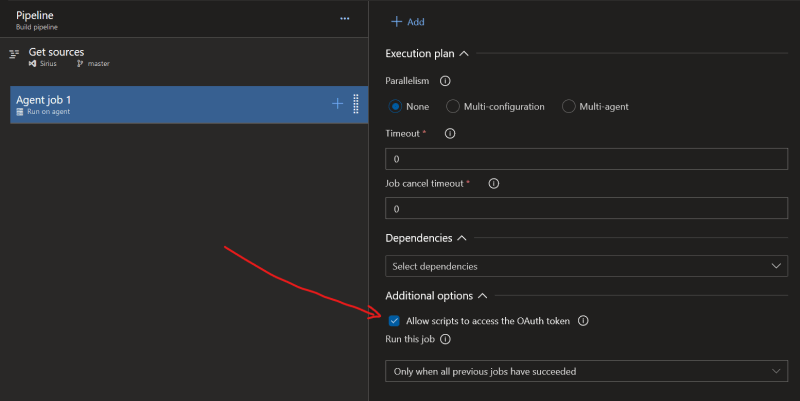 Enable access to OAuth token in scripts
Enable access to OAuth token in scripts
2. Create PowerShell Step
This is a very straightforward step - just add PowerShell task and select to use PowerShell Core (cross-platform version of PowerShell).
3. Register Package Source & Install Module
Now we need to add code for package source registration and module installation. Comments to the code are provided under the snippet.
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12 #1
$token = $env:SYSTEM_ACCESSTOKEN | ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText -Force #2
$credential = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential($env:SYSTEM_ACCESSTOKEN, $token) #3
$sourceName = "MyFeed" #4
$feedLocation = "https://pkgs.dev.azure.com/ochzhen/_packaging/myfeed/nuget/v2" #5
Register-PackageSource -Name $sourceName -ProviderName PowerShellGet -Location $feedLocation -Trusted -Credential $credential #6
$moduleName = "MyPowerShellModule" #7
Install-Module -Name $moduleName -Repository $sourceName -Force -Credential $credential #8
Get-HelloWorld #9
- Setting TLS version to 1.2 - there are known issues when lower versions are used by default, it is better to specify this.
- Converting our
AccessTokentoSecureString - Creating credential object that will be used to access our private feed.
- Name that will be used to register PackageSource.
- Location of our Azure Artifacts feed. Important:
../nuget/v2pay attention to the NuGet version, at the time of writing PowerShell doesn’t support NuGet version 3. - PackageSource registration
- Name of our module that we want to install
- Module installation.
- Using function from our installed module, here we assume that
MyPowerShellModulecontainsGet-HelloWorldfunction.
YAML Pipeline
With YAML pipeline it is not very different. In my opinion, it is even simpler. Below is an example of a step from azure-pipelines.yml.
Note: System.AccessToken needs to be passed through environment variable explicitly - see line #10.
- task: PowerShell@2
inputs:
targetType: 'inline'
script: |
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12 #1
$token = $env:SYSTEM_ACCESSTOKEN | ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText -Force #2
$credential = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential($env:SYSTEM_ACCESSTOKEN, $token) #3
$sourceName = "MyFeed" #4
$feedLocation = "https://pkgs.dev.azure.com/ochzhen/_packaging/myfeed/nuget/v2" #5
Register-PackageSource -Name $sourceName -ProviderName PowerShellGet -Location $feedLocation -Trusted -Credential $credential #6
$moduleName = "MyPowerShellModule" #7
Install-Module -Name $moduleName -Repository $sourceName -Force -Credential $credential #8
Get-HelloWorld #9
failOnStderr: true
pwsh: true
env:
SYSTEM_ACCESSTOKEN: $(System.AccessToken) #10
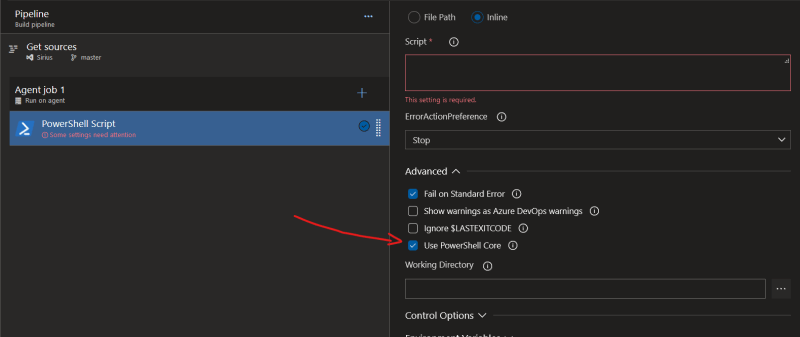 Create PowerShell step
Create PowerShell step