Use Azure PowerShell Module in Azure Functions - Quick Guide
Thanks to the PowerShell Core support in Azure Functions we can now also use PowerShell Az module in Function Apps.
To make PowerShell Az module available in an Azure Function, managedDependency property has to be enabled in host.json file, and Az='5.*' module version included in requirements.psd1 file.
It is great that now Azure Functions can be also used for infrastructure management and scripting. For example, recently I used it with Azure PowerShell to write a function that retrieves information about traffic managers in a subscription to power a simple dashboard.
IMPORTANT: This post is about using Az PowerShell module inside of an Azure Function with PowerShell runtime. It is NOT about managing Azure Functions with PowerShell.
Contents:
- Overview
- [Required] Enable managedDependency property in host.json
- [Required] Including Az Module in requirements.psd1
- Configuring Managed Identity
- Granting Permissions
- Connecting to a Subscription
- Editing Files in Azure Portal
- Useful Links
Overview
Using PowerShell Az module inside of Azure Functions is simple to achieve. There are two required steps that we need to do to make Azure PowerShell available in the function runtime: enable managedDependency in host.json and list Az Module in the requirements.psd1.
However, just having Az module available in an azure function is often not enough. Most likely, we’ll want to communicate with Azure and manage resources there. To accomplish that, we need to set up necessary permissions for the Azure Function.
One of the options is to configure system-assigned managed identity and grant necessary permissions to it on Azure’s side. Then in the PowerShell code, we can connect to a subscription and run commands.
Lastly, just a convenient thing, we show how to edit PowerShell Azure Function files in Azure Portal, for example, host.json, requirements.psd1, run.ps, function.json, and others.
[Required] Enable managedDependency property in host.json
We need to verify that managedDependency property is enabled in host.json, it is set to true by default when a PowerShell functions project is created.
When this feature is enabled, PowerShell gallery is used to manage dependencies, and the list of required modules is taken from requirements.psd1.
{
"...": "...",
"managedDependency": {
"Enabled": true
},
"...": "..."
}
[Required] Including Az Module in requirements.psd1
Since requirements.psd1 is used for determining what modules need to be installed, we have to specify our Az module and its desired version.
We can specify an exact version or only major version, in the latter case minor versions will be updated automatically.
@{
'Az' = '5.*'
}
Configuring Managed Identity
Managed Identity is a convenient and secure way to access Azure resources, it is managed by the platform which significantly simplifies developer’s life.
In this example we will use system-assigned managed identity for Azure Function but the process is almost identical for user-assigned.
Creating a system-assigned managed identity for a Function App is extremely simple:
- Go to “Identity” section
- Select “System assigned”
- Set status to “On”
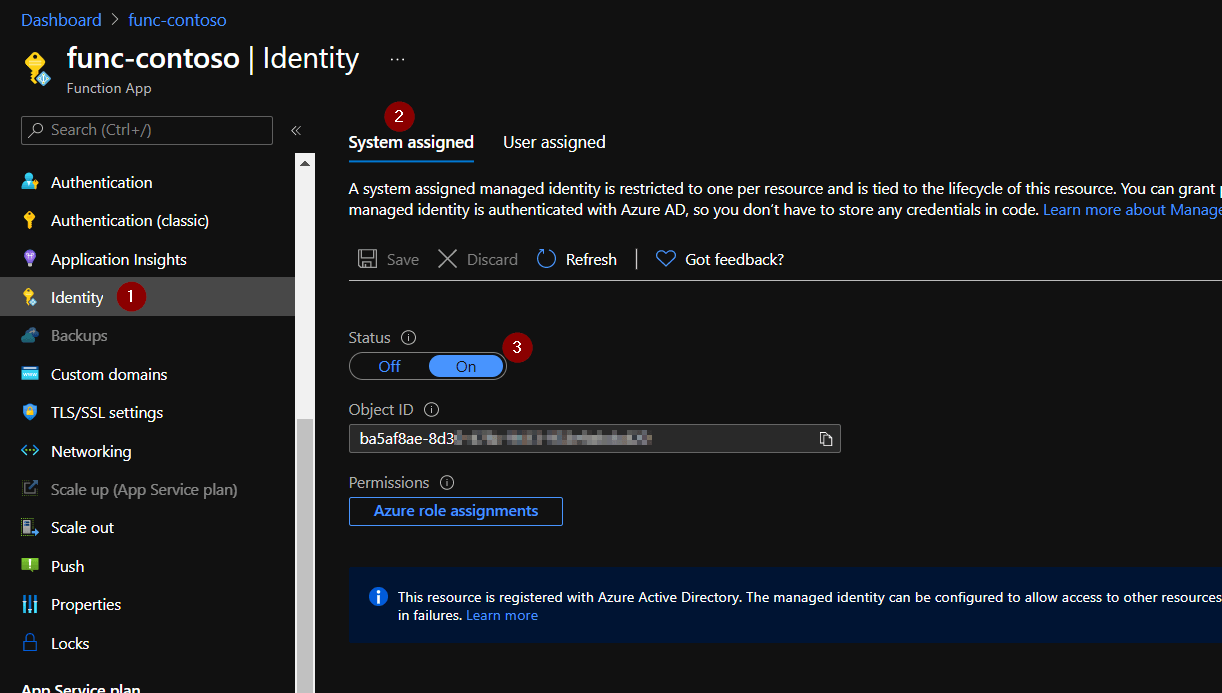 System-assigned managed identity
System-assigned managed identity
Granting Permissions
This step depends on what you want to access from the Azure Function, it could be an entire subscription, a resource group or a particular resource, read more about role-based access control.
Just as an example we will assign Reader role for a subscription to our system-assigned managed identity.
Here are the steps: Subscription > Access control (IAM) > Add > Add role assignment > Select Reader Role > Find managed identity by the Function App’s name > Save.
Connecting to a Subscription
It depends on the logic you want to run in an Azure Function but it is still quite likely that you’ll need to specify a subscription to work with, this is where your resources are. It can be done with Set-AzContext command.
An example is shown below, first we set the correct subscription and then retrieve information about a storage account.
Set-AzContext -Subscription "256e8e6c-8f2e-4153-8507-d9cd404b3728"
$StorageAccount = Get-AzStorageAccount -ResourceGroupName rg-contoso -Name stcontoso
Editing Files in Azure Portal
If you are just experimenting or doing some proof of concept, you might not want to set up and edit files locally, then publish to Azure. Luckily, in this case we can do it fully in Azure Portal.
Files host.json and requirements.psd1 can be edited under “App files” section on the Function App page. Just select the file you want to edit in the dropdown.
Similarly for function code in run.ps1 and function.json - edit them under “Code + Test” section of the function’s page.
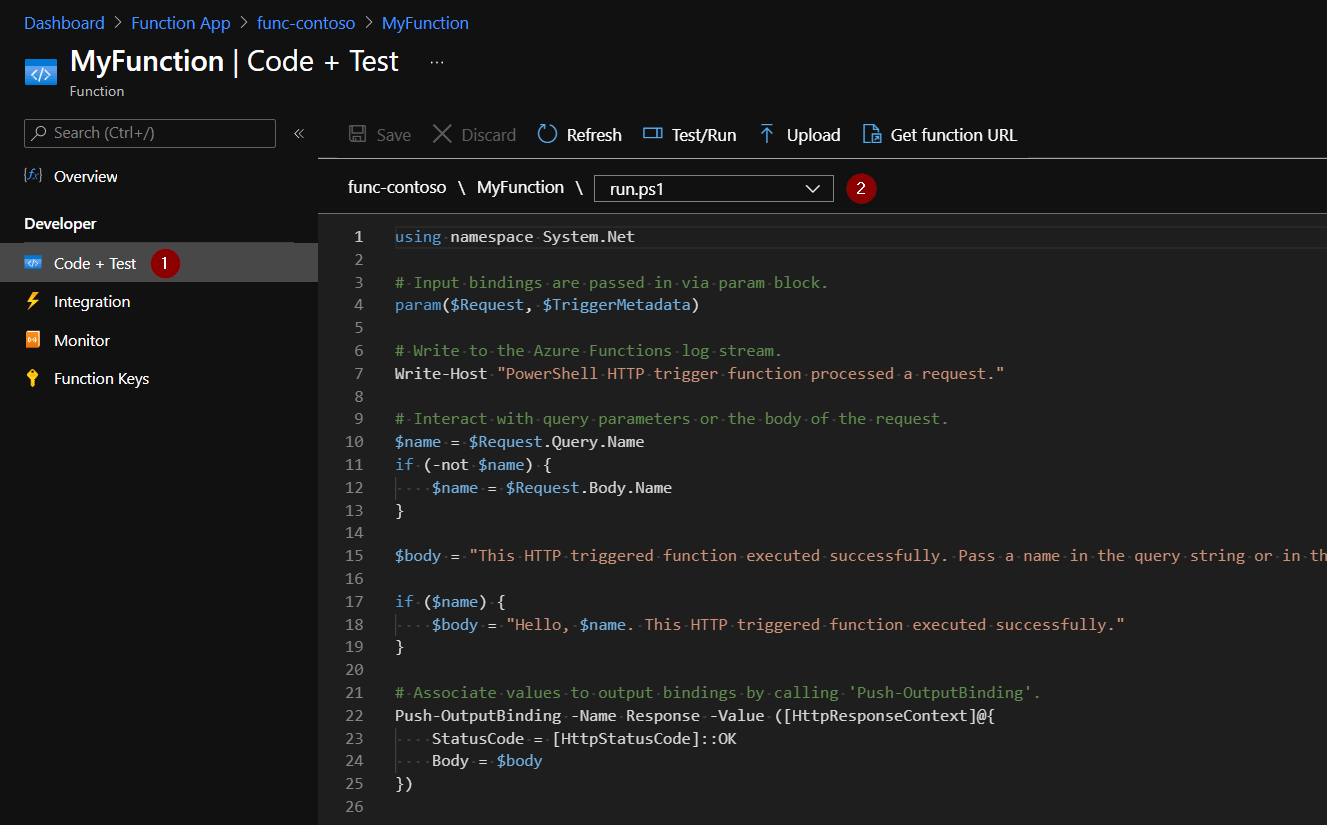 Editing function files in portal
Editing function files in portal
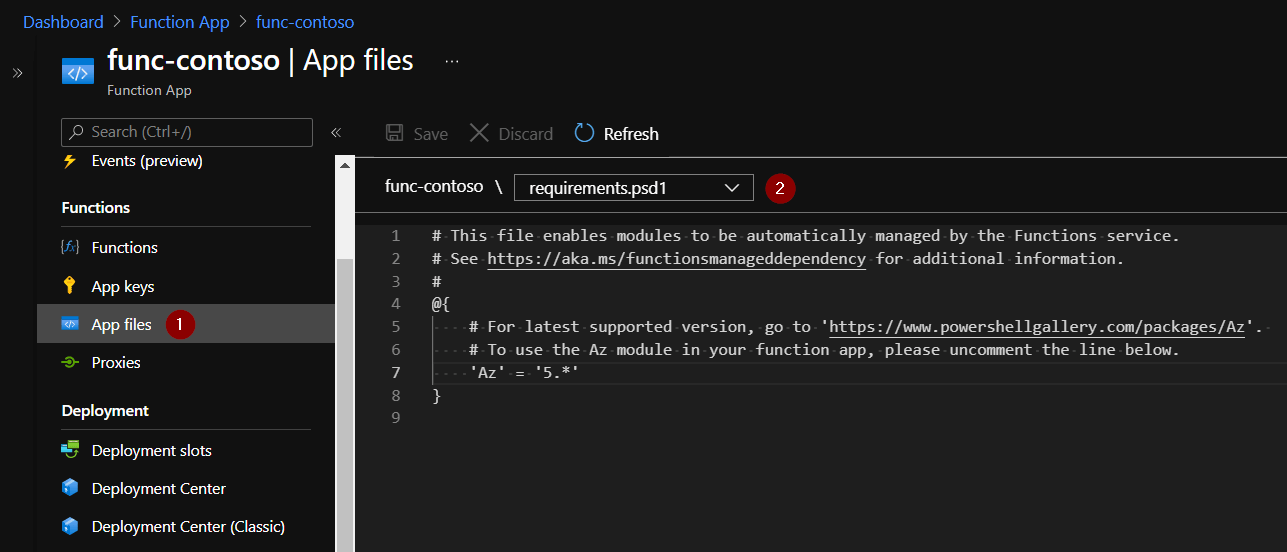 Editing app files in portal
Editing app files in portal